A Quick Fun Way to Understand the Basic Concept of Iterative Incremental Development
A fundamental aspect of Agility is incremental and iterative development. It’s so basic that when introducing Agile you usually mention this idea in the first 5 minutes. The core understanding that moving to small batches significantly improves speed, quality, and risk management, helps you move from an all-or-nothing approach to a world of options.
The challenge we are facing is how should we break down the scope. How should we define these small batches and construct them in the right manner? This challenge is surfacing with each new initiative. When I support and coach an organization moving to Agile, I find that people adopt the terms User Stories and Epics quite immediately, but the idea of incremental and iterative development is not really understood.
Lately, I have been experimenting with the use of the “Morning Routine Story Mapping” exercise Jeff created (which is also detailed in his book User Story Mapping: Discover the Whole Story, Build the Right Product and also quickly outlined here as the “getting out of bed” and out the door game”). the game is a major success for Product Ownership workshops when introducing the story mapping technique.
Jeff Patton has always been a source of inspiration to me with his brilliant post on iterative and incremental development Don’t Know What I Want, But I Know How to Get It, using the Mona Lisa creation process as a metaphor, which I continually refer to, especially when training in France.
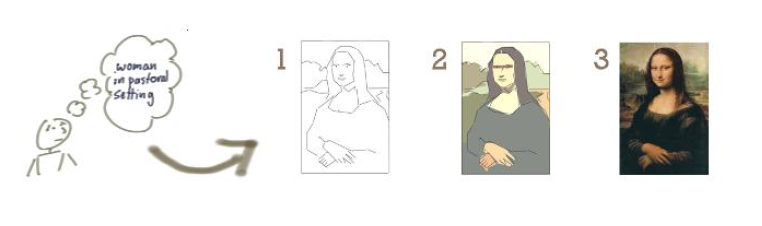
I started running this exercise when introducing Agile and not only in the Product Ownership workshop. This collaborative exercise demonstrates the right way to slice the product into meaningful increments and I found that it’s a very quick and effective way to convey this fundamental idea of Agility from the beginning to all stakeholders.
The exercise is interactive and is raising the energy levels of the participants. to my surprise, the exercise also serves as a great ice breaker and team builder since it creates the opportunity to get to know each other better by exposing each other to morning habits and personal context, such as where I live, who prepares breakfast for the kids, whether I’m used to doing Yoga or never miss my favorite podcast…or any other thing people choose to do in the morning – so it becomes really funny and fun.
Here are the steps I take to run the exercise:
Step 1 – Individually list the morning activities (5 minutes):
I ask people to write on sticky notes the activities they did from the moment they woke up until they reached the office, as many as they can.
It should be one activity in each sticky note and should be done individually (unless people woke up together that morning …)
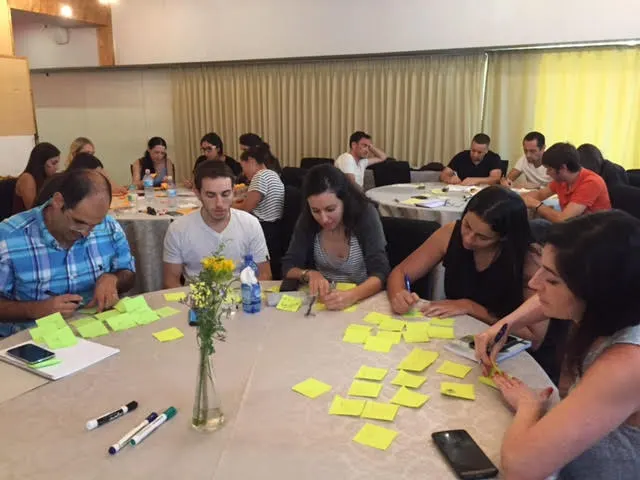

Step 2 – Collaboratively grouping the activities (5 minutes) :
I choose a space in the room with enough place on the wall. In teams of up to 7 people, I ask people to take their notes and group them together under a common topic that will be their title. It’s a group of activities with a common goal, for example, washing and refreshing can include activities such as brushing the teeth, taking a shower, going to the toilets, etc.
Each team should place their sticky notes on the wall and organize them in groups with the topic as their title. The titles are the “backbone” activities.

Step 3 – Order the group of activities by time (3 minutes):
I ask the teams to order the activities from left to right sequentially, in a way that the order makes sense as a story with a beginning, a middle, and an end (for example wake-up, washing, breakfast, home arrangements, kids, travel, reach the office..).

Step 4 – Order the activities by criticality (5 minutes):
Now I ask the teams to prioritize the activities in each group by criticality ordered from top to bottom so that important activities are on top.
Briefing on this step:
Prioritizing is difficult when there are no guidelines, such as a certain goal we wish to achieve with our product or a certain market segment or specific persona. For example, if our target customers are single men under 25 with no kids or married women with 3 kids over 30 — the priorities will probably be different, and different activities will be considered critical for each target customer. Define the goal/persona so it is easier to determine the priorities.
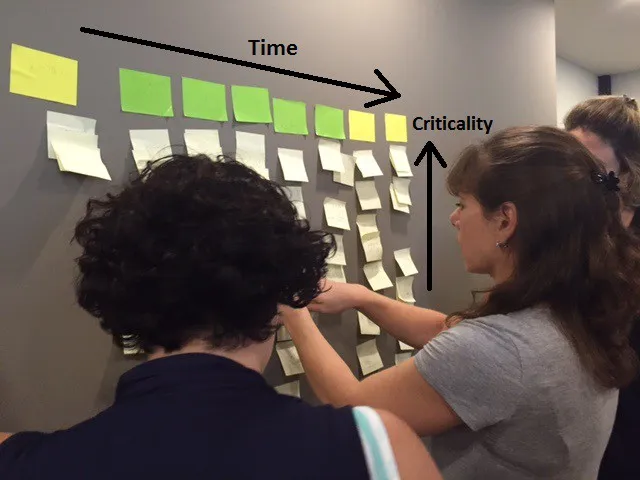
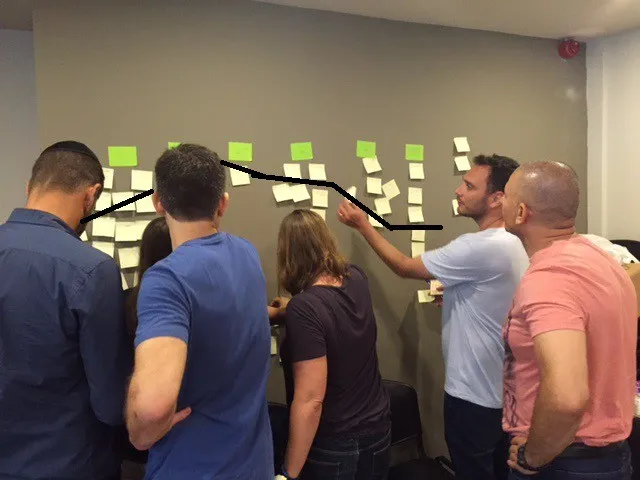
Step 5 – Drama! (5 minutes):
And now for the drama.. I tell the group:
Imagine you had a very important meeting in the morning that you just cannot miss or be late to. Unfortunately, the alarm clock didn’t do its job and you woke up late and have only 15 minutes to get out of the house!
What do you do? Which part of the morning routine will you drop to fit in the minimal time you have?

Now I ask the team to draw a horizontal line through the activities so that all the activities they choose to do in such a morning are above the line and all the rest under the line.
They need to reach the office safely and be on-time with the minimum activities as possible.

Final Briefing:
The exercise demonstrates the following important concepts:
- With the constraint of time, our aim is still to realize the full “value” of getting on time to the office. In the process of minimizing the activities, we removed many of them in each step and left the process very thin and lean but still end-to-end.
- Since we have a time constraint, we eventually want to be fast, which means minimizing the time to reach value. in many cases, we will go too deep in a single step and not realize the full end-to-end value. in this exercise, we demonstrate how it should be done across the map and how in every increment we build we have the full end-to-end.
- We don’t invest equally in each step – in some steps we left only one activity and in some we left more, depending on the step. Some steps were even entirely removed.
- Choosing the depth of each step is easier when the full picture is available since the alternatives are visible.
- Focusing on a single activity but in the context of end-to-end value helps development teams better understand the scope of the requirement. For example, preparing breakfast in the context of getting out of the house in 15 minutes is totally different from preparing breakfast for the family on a vacation morning. Communicating effectively the context helps to make the scope more precise and to trim the less important parts of the scope.

Every time I run this exercise people approach me and say things like “Now I got it” or “if we followed this approach in previous projects it would really help” and they have many ideas on how to do things differently
Enjoy and good luck.
See our Agile Games and Exercises page for more.