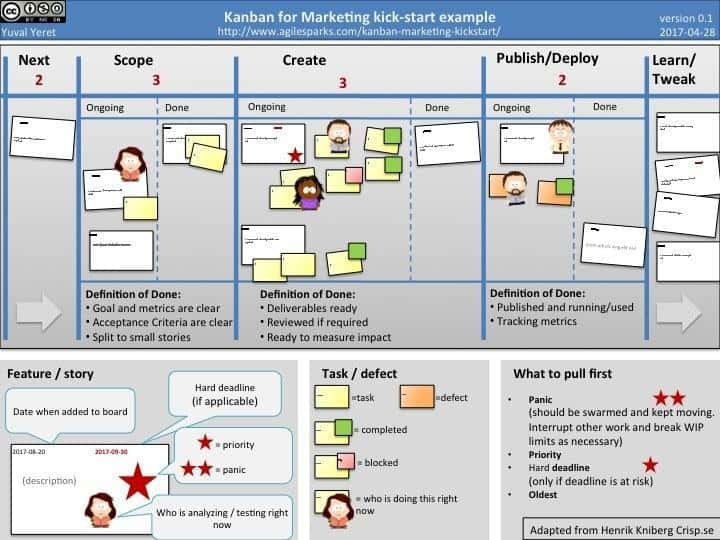
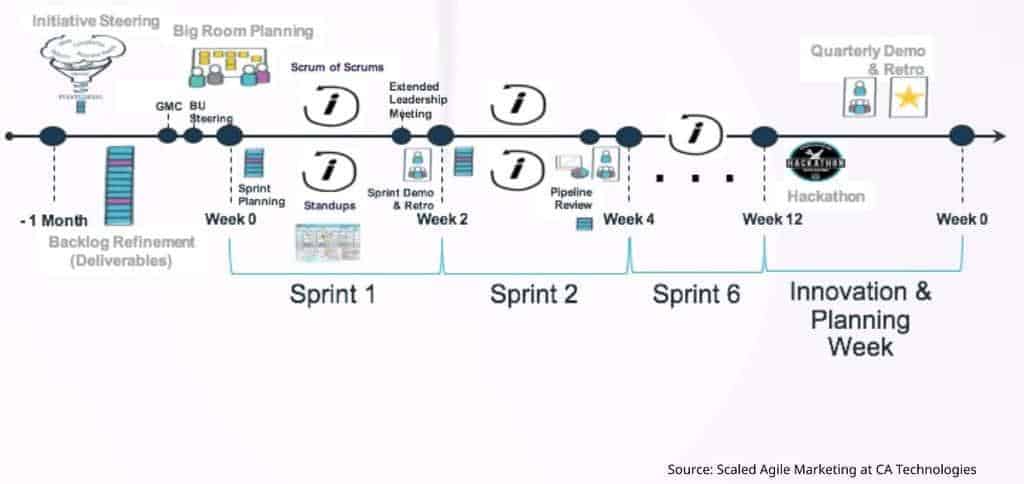
Defining Agile Marketing
In this article, we will try to define the approach known as “Agile Marketing” – The application of ideas from the world of “Lean/Agile Software Development” to the world of marketing with the aim of achieving marketing agility.
What ISN’T Agile Marketing
First, a couple of clarifications and myth-busting. Agile Marketing isn’t reactive marketing. Agile Marketing isn’t about how you react in a Marketing/PR crisis (ask United about those) or real-time opportunity (you can ask Oreo about those). I don’t mean that you can not/shouldn’t deal with those when you’re doing Agile Marketing, but it isn’t what Agile Marketing is about.
Agile Marketing also isn’t “We just get things done without any real process”. You could say your marketing department is agile in how it deals with emerging needs and very responsive and it might be working great for you. But it’s still not necessarily capital-A Agile Marketing!
Agile Marketing isn’t also Scrum. Agile Marketing isn’t Daily Scrums/Standups, Sprints, or Scrum Masters. Agile Marketing also isn’t using a Kanban board to manage marketing. Agile Marketing isn’t a methodology or even a framework.
So, What IS Agile Marketing?
I like to think of Agile Marketing as an approach. Based on the same thinking and mindset behind Agile Development, Agile Marketing manages uncertainty through iterating, anticipating, and adapting.
In an earlier post, I described several challenges marketing organizations are facing. If you look at them more closely you will see that many of them arise from a significant growth in uncertainty that these organizations face. around both WHAT marketing would work as well as HOW to build it in an effective way.
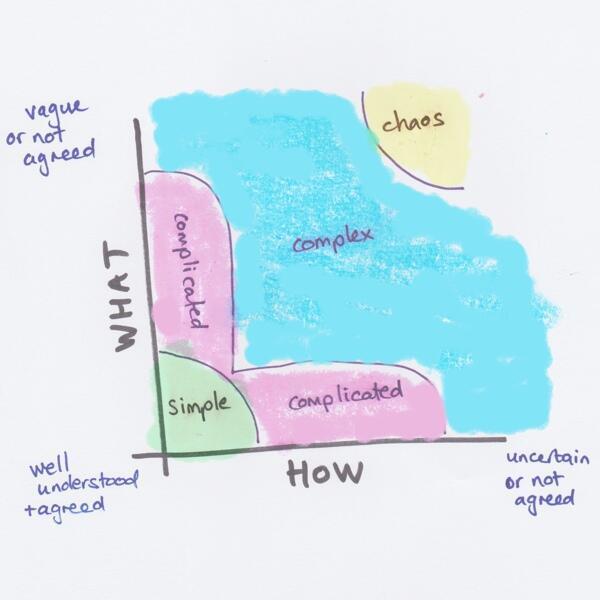
Dealing with uncertainty around WHAT marketing experience to deliver
In the diagram above, called the Stacey Matrix (see a description by Sam Laing back in 2013 or on my personal blog), WHAT relates to questions around what our customer journey experience should look like. well understood and agreed on means that we have very high certainty around what experience would drive our customers through their journey in the fastest most streamlined way. vague or not understood means we might think we know but we’re not sure, or even worse we’re oblivious to our gap of knowledge. In the age of the “Digital” experience, the explosion of channels, as well as the pace of industries are being disrupted and forced to change, figuring out what constitutes an effective experience is becoming a harder and harder challenge.
Dealing with uncertainty around HOW to deliver the marketing experience
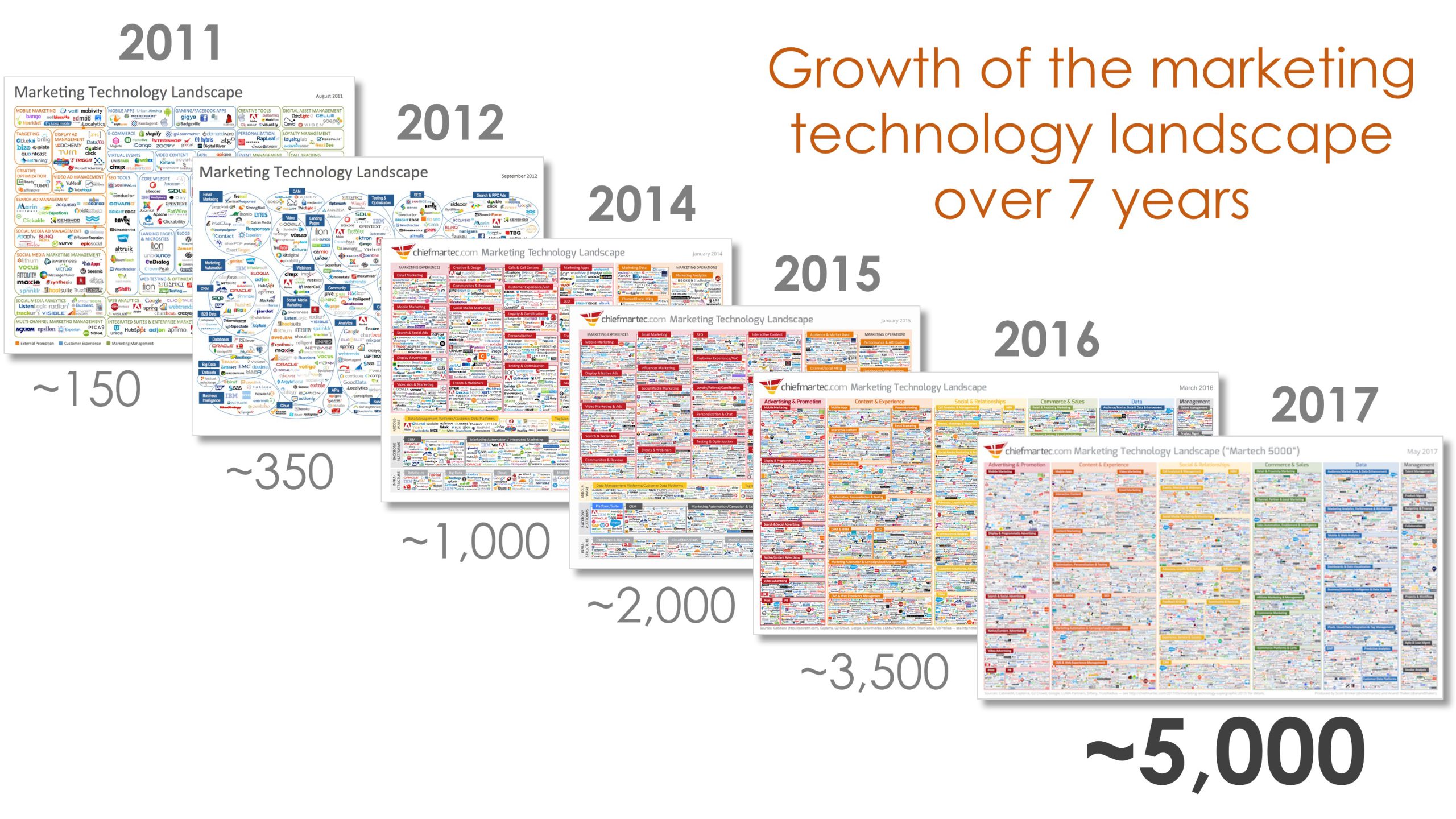
HOW relates to questions around implementation. Here, a big part of the challenge is the growth of the marketing technology stack. As Molly Walsh asks, How the heck did we get here? Most marketing organizations are struggling to implement their marketing plays. The more technologies in your stack the more moving parts, and the more uncertainty around how to fit the pieces together.
As you can see, once you have both WHAT and HOW uncertainty, you’re well into the complex space. In the complex space planning up front wields limited results as you can’t predict what would work in advance. You can plan your objectives/goals/investments but even that would change as the landscape changes.
Agile Marketing – Anticipating Complexity/Uncertainty and Dealing with it using Iteration/Adaptation

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

The Agile Marketing Manifesto emphasizes/values some new approaches to marketing that are replacing some well-entrenched marketing conventions. This is actually aligned with what Marketing leaders such as Sergio Zyman have been advocating for. If you read Sergio’s “The End of Marketing As We Know It” from back in 2000 you will find hints of Agile Marketing!
Validated Learning, Customer Discovery With Many Small Experiments, Leading to Adaptive and Iterative Campaigns
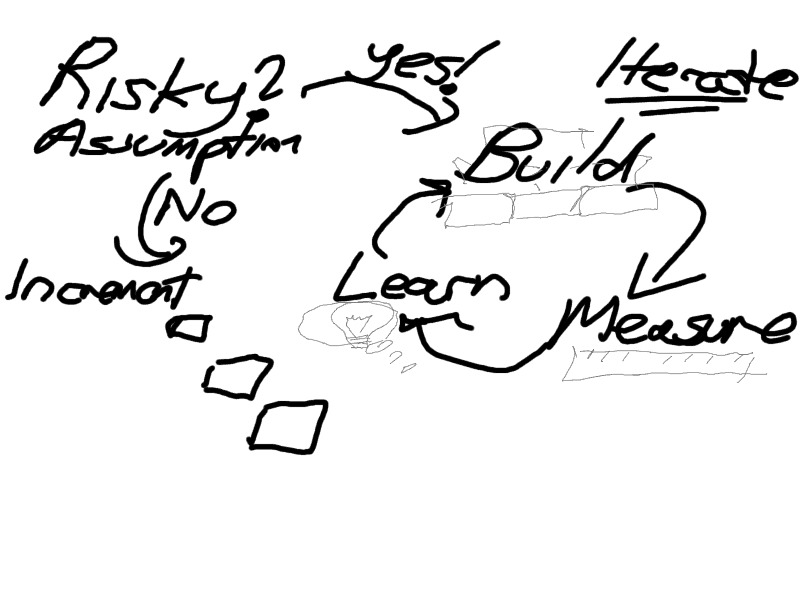
The Agile Marketing Manifesto introduces concepts such as validated learning (which is brought over from the Lean Startup approach) – replacing decisions made just based on opinions and conventions with a process of looking at each marketing play, identifying risks/assumptions, then for the risky plays going into a Build-Measure-Learn experimentation iterative loop where marketers try to validate as quickly as possible whether their thinking and assumptions are correct. Upon validation, the play can be completed and scaled. In case of invalidation, the play can be tweaked/changed in what is called a “Pivot” to continue to look for a winning play. This is called “Fire bullets (and only) then fire cannonballs” in Jim Collins’s Great By Choice. When there’s less risk, it still makes sense to deliver incrementally – you want to minimize the cost of delays between the time you decide to execute a marketing play/campaign and the time you’re able to go to the market. If you can deliver some minimal play/campaign that can already start to have an impact on your customer journey/brand, you want to do that.
Agile Marketing Isn’t Easy To Digest
This seemingly goes against marketing conventions like “nailing the perfect campaign and only then launching it with a big bang” and “protecting our brand by only releasing high-quality marketing content”.
Why seemingly? because in spirit the agile marketing approach actually is more aligned with the rationale behind these conventions.
Using adaptive iterative campaigns leverage small experiments to make sure “we nailed it” and only then “launching with a big bang” still looks like a “big bang” to most of the market.
In addition, you get the advantage of having a higher chance of success since it was validated in the real world, thereby actually protecting the brand by reducing the chance of spectacular failure upon the big bang launch. (e.g. Pepsi’s controversial ad or New Coke – both smartly pulled from the market pretty quickly after considerable sunk costs).
We HAVE to be able to adapt.
It might feel uncomfortable but we must find a way to do it. The key to doing it well is to slice experiences in a way that you’re still delivering a great experience but only for a small slice of the market or some part of their needs but in a way that is representative of the wider audience/experience so that you can learn and improve your plans/designs based on it. (e.g. just in one city, just for one type of user of your product, just as an experiment in one airport, whatever).
Being able to craft meaningful high-quality experiences that are still smaller than the “full thing” is one of the non-trivial yet important skills of the agile marketer.
There’s a lot of applicable learning in this domain from what startups and enterprises are seeing trying to adopt “Lean Startup” and “Minimum Viable Product” thinking but it comes down to innovative creative thinking by marketers to come up with the right tactics that can help them test their strategies without risking the brand or diminishing the overall impact of the overall marketing campaign.
Customer Focused Collaboration
Agile Marketing brings together marketers and other players to collaborate on improving customer experiences. If you were ever a sole marketer for a company or part of a marketing team for a small startup/company you know what this looks like. You can move much faster when everybody you need to deliver the overall marketing impact is on your team (or in your head). Most marketing organizations lose this advantage when they grow beyond the single team and specialize.
Agile Marketing requires Lean/Agile Leadership
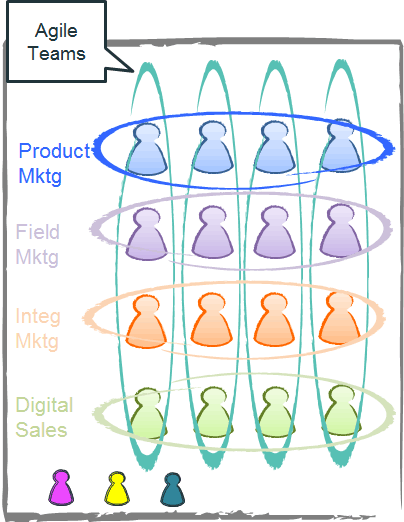
Agile Marketing tries to bring back this effectiveness, speed, fun, and focus of the small startup regardless of your organization’s size. We create autonomous agile marketing teams that are empowered to make local decisions aligned with achieving their goals while doing what’s right for the overall brand. This only works if we:
- build the right competence by hiring the right people and encouraging them to master their domain and giving them the space to learn and improve
- create high clarity by sharing the business context, our vision, and constraints.
This autonomy and new structure don’t mean there’s no need for marketing managers/directors of course. It does mean changes in their focus e.g. on things like hiring and nurturing great marketers and providing clear and meaningful mission/purpose.
Customer-focus teams can take many shapes
Those customer-focused teams on aspects such as:
- the whole customer journey for a certain brand/product/market (e.g. SMB)
- Content Creation, Publication, Measurement
- A key marketing challenge/opportunity such as a stuck Middle of the Funnel (MOFU), or ineffective Sales Enablement.
- Account-Based Everything (ABX)
- Planning and delivering the company’s Customer event or presence at a key industry event
- Exploration of a new marketing approach such as “Social Selling”, “Video”
- A key marketing KPI that is not performing well or is identified as a key objective for growth.
While we call it Agile Marketing, in many cases these teams include and involve participants from other adjacent functions such as Inside Sales, Product Management, and Customer Success.
From tasks to Customer-focused stories
Once the marketing organization’s work structure is oriented toward a customer focus – Agile Marketers start managing their work in a customer-focused way as well. They use work items that reflect marketing value such as “User Stories” or “Job Stories” rather than “to-do lists” or “tasks”. Thinking of work in this way and including the goal/impact expected of each work item as part of the “Story” helps marketers maintain a laser-focus on the customer impact they’re aiming for the day in and day out. This also makes it easier to communicate with business stakeholders about what marketing is focusing on and get their early feedback and guidance – which helps avoid the common situation where marketers talk in language that business/sales don’t care about and after delivering something there are still major gaps between what the business/sales expected and the marketing that was delivered.
Agile Marketers also use more disciplined and more customer-focused prioritization mechanisms that take into account considerations such as Cost of Delay, Time Criticality, Opportunities as well as Risks addressed to consider what to focus on next and whether to interrupt ongoing work for an emerging opportunity.
Continuous Planning
While some marketers understand agile marketing to mean “no planning” this is not the intent. The Agile Marketing Manifesto talks about “Responding To Change” over “Following The Plan”. Another way to look at it is “Flexible” or “Continuous” Planning vs “Rigid Static Planning”.
Planning in Agile Marketing happens at two levels.
One is planning what to work on and what we can commit to delivering for a certain timebox – be it a day, week, quarter, or year. Let’s call this cadence-driven planning.
The other is focused on a certain marketing campaign/play – planning the strategy, vision, tactics, and rollout plan for that campaign/play. Let’s call this content-focused planning.
Sometimes most content-focused planning happens during cadence-driven planning but that’s not a must. It might make more sense to do the content-focused planning just in time as we start a campaign/play and not at the beginning of the quarter.
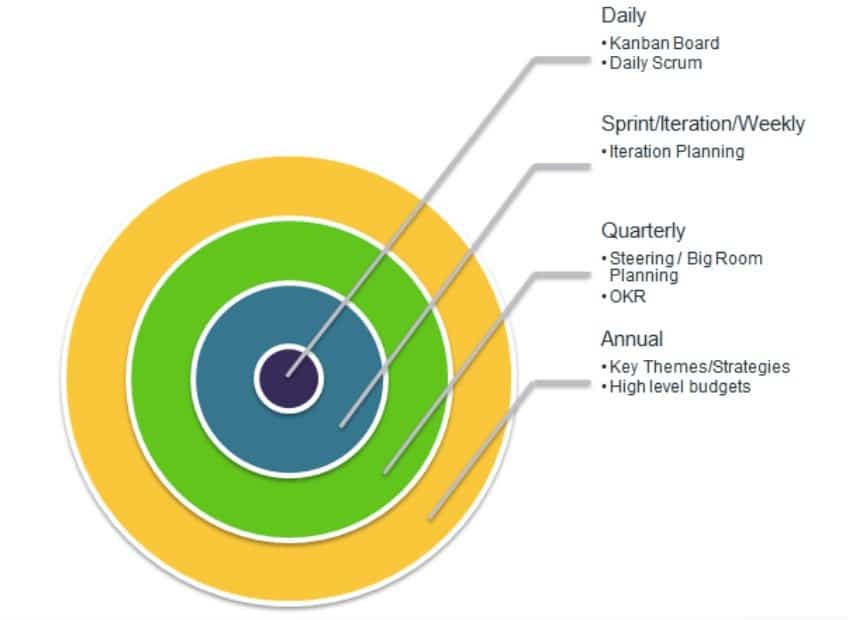
Agile Marketers use a combination of Kanban, Scrum, and sometimes a higher-level framework such as SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) as their main techniques for dealing with these different planning and execution management levels.