Intro
Earlier this month I was helping a software organization in an Israeli defense organization (that’s why there are no pictures) run their first PI Planning event. The day after I told my colleagues at Agilesparks that this is one event I will try to remember whenever I get into difficult times doing coaching, something that happens from time to time, coaching being what it is. I will try to remember that day because of the magic that happened somewhere around noon. And I want to tell you all about it.
If you aren’t familiar with it, PI Planning is an event where the entire (yes, entire) organization (or part of the organization, if it is big, up to around 125 people) convenes for 2 days to plan the next 4 to 6 iterations (sprints). Most people, hearing about it for the first time, respond in the exact way you did just now – incredulity. Yet, at the end of the event people are just talking about how will they make the next time even better. Having said that, the event we did this time was one day only – you need to choose your battles. As you will see, we needed that extra time.
Warm-up
The main purpose of the PI Planning event is to align and synchronize the organization and so the first day opens with overviews by various stakeholders, product managers and architects, all bringing concise messages and information – we don’t want all the people sitting there getting too bored, a challenging task. Immediately following this the teams break out for planning. Everyone stays in the same venue, huddling around tables, trying to come up with content for each of the PI’s iterations (leaving the last iteration for other things.) And here things start to warm up.
At the beginning the teams will usually stay together, calculating their capacity for each iteration and better understanding the required features to develop. However, after an hour or so it starts to be evident that there are dependencies on other teams, and this is exactly what happened at the mentioned event. One of the reasons the organization went into this in the first place is that coordination and alignment between teams did not fare so well. Yet, even though it was obvious the dependencies should be discussed, teams preferred to continue and look at their own plans, keeping to their tables, exactly like other teams in other organizations do.
Enter the program board
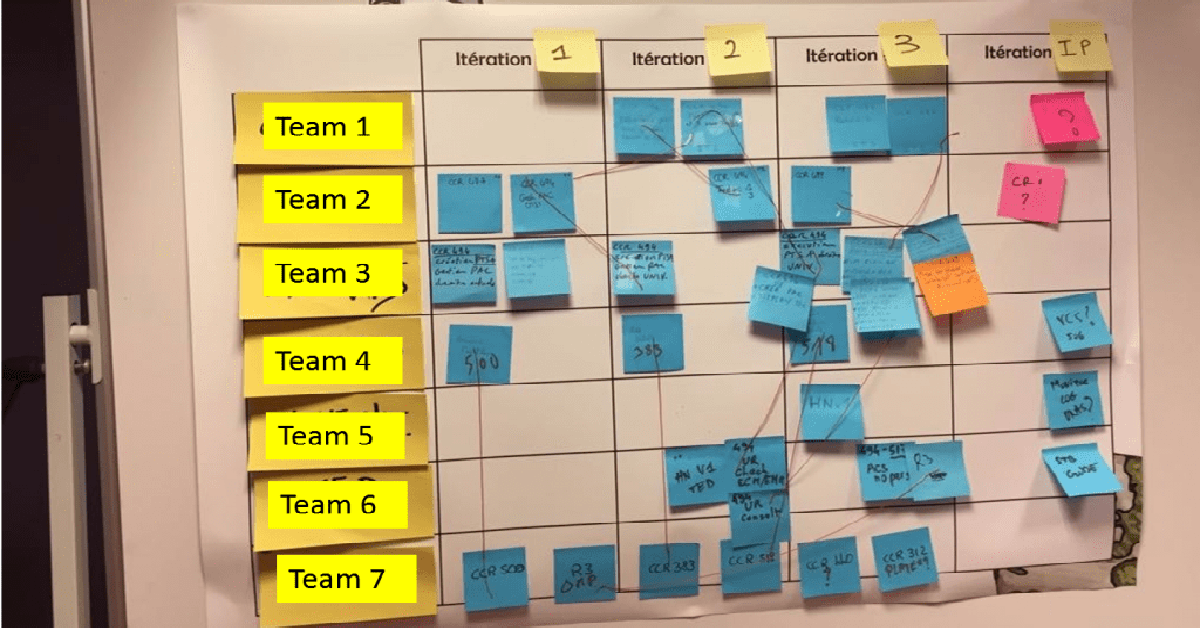
This is a good time to mention that another output of the event, in addition to the team’s plan, is the program board on which we clearly see dependencies between the teams. At this point of the event, the board was empty. Seeing the situation for what it was, the RTE, a sort of a scrum master of the scrum teams, started going around the tables, prompting people to start placing dependencies on the board, assertively. And so they did. And then magic happened.
We asked teams that placed dependencies on the board to make sure they talk about it with the relevant teams (people and interactions over processes and tools, right?) and this started an interaction across the teams. While at the beginning the noticeable huddle was around the program board, soon you started to see people from different teams at other teams’ tables. It was not just scrum master to scrum master but any representative with any other team members. People were thinking about where should they move this story and whether they could split that feature to accommodate for the dependencies. Suddenly you saw how decision-making went down to the ranks, how they took ownership of the big plan.
Self Organization Magic
That magic of self-organization was happening right before our eyes. Instead of some managers making all the decisions and being the pipelines for messages, people were interacting directly. Later the RTE said that while she felt she was a bit losing control of the happenings, the volume of interactions and decisions was something that couldn’t be tracked by one person. She was happy.
At some point it seemed as though energy is starting to go down and that we can start to wrap up. The RTE called for a scrum of scrum meeting around the program board where some dependencies were not handled. We gave the teams another 45 minutes.
The Confidence Vote
Once we had everyone’s attention – it was not an easy task – we asked the people to raise their hands in the air and indicate with the number of fingers what is their level of confidence in the plan. One means no confidence at all, and five means excellent. As hands went up in the air we saw one One and a few Twos. Most were from one team. We asked the people what was the issue and the response we got was that everything got into the plan because this is what they were asked to do. Not good.
What the RTE did at this point was to allocate another 30 minutes for the teams to change their plans so they will believe in them. Stories were moved, features got a bit thinner and when we had the vote again, we had a few Threes and the rest were Fours and Fives. The number of Threes was small enough for us to decide to handle these issues during execution.
Retrospective
At the very end of the day, we asked the teams to present the main findings of their retrospective. The feedback was good, mainly that teams agreed on them when and who will do what is something that so far they couldn’t manage to do. This fast coordination loop is making things that would usually take weeks or months to happen in one day. And that’s magic!