Focusing on SAFe™
In the previous article in the Scaled Agile Marketing series, I provided an overview of how Scaled Agile Marketing looks like. This time around I want to provide some more details on one of the approaches I mentioned for implementing Scaled Agile Marketing – the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe™).
Why SAFe? First of all, it is the most popular scaling approach these days and so many marketers will find themselves in organizations where SAFe is actually used in IT/Technology and the option of using it in Marketing as well will come up. As a result of that, it is also the scaling framework I’ve actually had a chance to use in a marketing context with good results.
Let’s make sure we cover the SAFe Essentials
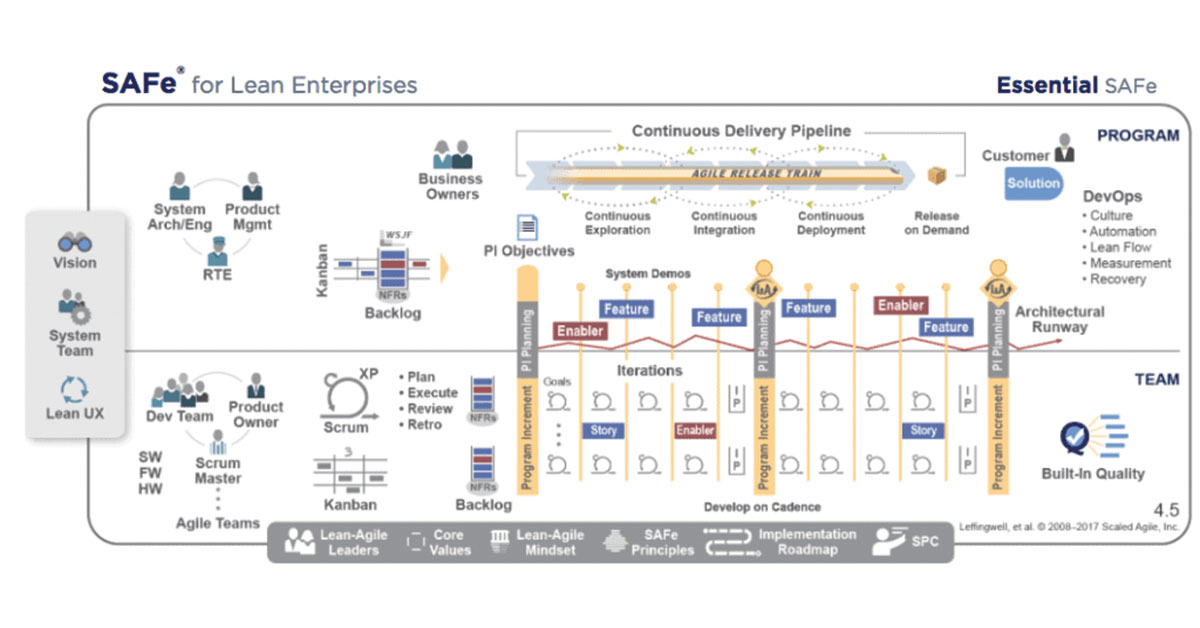
SAFe has several configurations that can range from the “Essential” configuration through “Portfolio” and “Large Solution” configurations all the way to “Full SAFe” which includes all configurations together. In this article, I will start with the “Essential” configuration and mention “Portfolio” towards the end. The “Essential” configuration isn’t just a version of SAFe it is also a set of 10 essential elements without which you might be scaling agile but you aren’t really using SAFe to do it.
I actually covered some of the essential elements in the previous article:
- #1 Lean/Agile Principles
- #2 Real Agile Teams And Trains (In the “The Agile Marketing Team of Teams” section)
- #3 Cadence and Synchronization
- #4 PI Planning (covered in the “The Agile Marketing Team of Teams” section as well)
- #7 Inspect and Adapt (Learn at the System Level)
- #10 Lean-Agile Leadership
So let’s look at the remaining essential elements:
- #5 – DevOps and Releasability
- #6 – System Demo
- #8 – IP Iteration
- #9 – Architectural Runway
#5 – DevOps and Releasability -> MarOps and Releasability
This is essential that requires slight tweaking for a Marketing context: SAFe Agile Marketing organizations aim to break down silos between marketers and marketing technology (MarTech) and operations. Each Agile Marketing Train should be able to continuously run marketing experiments or deliver new marketing plays/campaigns to the live customer/buyer journey. Over time, the separation between marketing and marketing tech/ops is significantly reduced and marketing trains operate with an automated continuous delivery pipeline that includes easy instrumentation and measurement to enable continuous experimentation and validation of hypothesis.
#6 – System Demo
When we defined Agile Marketing we talked about some of the key things we value – “Validated Learning”, “Customer Discovery”, and “Adaptive Campaigns” among others. One value that isn’t explicitly mentioned in the Agile Marketing manifesto but is implicitly required to achieve these is “Working Marketing” meaning objective observation of working marketing deliverables rather than lengthy comprehensive documentation/designs/plans. I used to tell agile development teams that unless they’re the Microsoft PowerPoint development team their demos shouldn’t be running PowerPoint. In a marketing context, I cannot say that anymore because sometimes a PowerPoint deck IS the marketing deliverable but you get my drift.
We should frequently look at real marketing deliverables so we can discover whether they really drive the customer journey experience we are looking for as well as get a real feeling as to progress towards our goal. In a scaled context where we have multiple marketing teams working on a larger customer journey or marketing campaign, it’s crucial to frequently integrate the whole marketing story using real deliverables, get some feedback on it, and adjust course if necessary. This is the intent of the System Demo in SAFe. Every two weeks, the full system – the integrated work of all teams on the marketing train for that iteration – is demoed to the train’s stakeholders. Stakeholders provide the feedback the train needs to stay on course and take corrective action. In a marketing context, we probably need a better name for this. Any suggestions?
#8 – IP Iteration
The Innovation and Planning iteration occurs every Program Increment (8-12 weeks typically). Since we don’t plan specific content for the IP iteration it can act as an estimating buffer for to help meet your PI objectives. In addition, it provides dedicated time for innovation, continuing education, PI planning, and Inspect and Adapting events.
#9 – Architectural Runway
In product development, Architectural Runway refers to side work that needs to happen to support in order to support the fast and clean implementation of high-priority near-term features. In a marketing context, it refers to marketing technology/infrastructure that needs to be in place to support upcoming high-priority marketing plays/campaigns/activities (think for example a lead nurturing solution in case we plan to do lead nurturing in the next PI), exploration/research, and maybe some key architectural components like a page template or a slide deck template or brand guidelines that reduce the amount of effort when getting to work on actual marketing plays.
Essential SAFe works pretty well in a Marketing context, with some limitations
As you can see applying the 10 essential SAFe elements to a marketing context isn’t too hard. There are some modifications but at this high level, the mapping works. This doesn’t mean that Agile Development is Agile Marketing. What it does mean though is that once you have a good team-level agile marketing process/structure, there’s good applicable guidance for how to scale it. This is exactly what we’ve seen in CA Technologies when we applied SAFe to a marketing context. Our main challenge was and is changing leadership mindset, especially around decentralized control and organizing around customer focus and de-emphasizing the marketing specialties/silos as well as driving a real learning/experimentation mindset and process at all levels.
When it comes to leveraging SAFe the main challenge we had is that SAFe was designed for a product development context and therefore the materials and knowledge base which are one of SAFe’s biggest advantages weren’t a good fit for us. We actually started to use one of the SAFe’s workshops to train the teams but realized midway that there’s too much development language and examples so until we create either a more neutral version of SAFe or a marketing-focused variant, the best we can do is leverage the practices without relying on the great materials. It was also apparent that marketers prefer lighter-weight methodologies/frameworks and mainly didn’t have the patience to learn about SAFe in depth. The essential elements were all that could fit their attention span.
This combination of incompatibility of the materials and the distaste for formal lengthy training and a large set of practices also meant that when it came to SAFe expertise it was crucial to have people around that don’t just recite the SAFe gospel but also have a deep understanding of the principles and are able to adapt SAFe to other contexts without killing its spirit.
This is of course true for scaling agile marketing in general, regardless of whether you’re using SAFe, LeSS, or any other approach. You’ll be working in exploration mode trying to identify the right language, process, and structure. In most cases, marketing people will give you limited attention. Make sure you have somebody that can support you in that mode rather than just teach you a methodology.
There’s one thing I would always add to Essential SAFe
Yes, I know, the thinking is to keep it to bare essentials, and 10 elements is better than 11, but there’s one key concept and practice that is part of SAFe, is portrayed in the Essential SAFe big picture above, but isn’t mentioned as a key element here. It is also one of my favorite focus areas. Enough clues for now. I’ll let you try to figure that one out until the next article which will focus on this topic…