The complex reality presents many challenges and dilemmas that Scrum Masters and leaders at all levels try to solve using problem-solving techniques. Yet dilemmas are different from problems. While problems have a good answer or solution, dilemmas have more than a single good answer.
We are all familiar with dilemmas like Centralized vs. Decentralized, Cross-functional vs. Professional-focus, Quality vs. Speed, Individual improvement vs. Team improvement, Continuity vs. Transformation, Task-focus vs. relationship-focus, and many more.
In this article, I would like to present an easy and useful tool that managers at all levels can use to find a win-win answer. Scrum masters and managers that are required to lead in the complex VUCA (Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity) world can use this tool to select the right stance to take.
To better understand this, let’s look at the following picture:
Some people see this picture of an old lady and some see a young lady, but both are there.
What do you see? Can you see both?

Not many people can see both at once. In 1975 Barry Johnson developed the Polarity Map© as a way to understand and thrive in polarized situations.
Let’s discuss one common polarity dilemma SM’s and managers cope with and learn a tool that will help them improve the way they lead in this complex world.
“Make it Done” vs. “Empower others” To map the polarity, we use two blocks each representing one approach (=pole), designated in the middle of the block, of the polarity.
The upper part of each block presents the respective benefits (+) which support achieving the goal of “Great Manager” (in this example). The bottom part of each block presents the negative consequences (-) of overusing that side of the polarity.
(see the picture below)
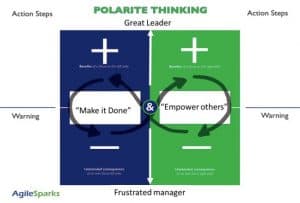
Let’s see how it works:
SM’s and managers understand that the “Make it Done” attitude is one of the reasons they were promoted to this position and therefore focus mainly on this side of the polarity as their style of leadership. By taking the “Make it Done” approach, they reduce discussions and sync meetings, have more control on the way things are done, and ensure they are done in the best way they believe it should be done.
the negative consequences (-) related to the “Empower Others” pole, convinces them to stick to the “Make it Done” approach to leadership.
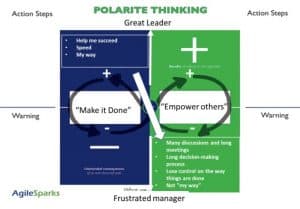
However, by over-taking the “Make it Done” approach, managers get frustrated. They realize that they are firefighters, they need to be available at all times to solve ongoing issues, no one takes responsibility and they don’t have enough time to complete the work they need to do.
This is the disadvantage of overdoing “Make it Done”.
This frustration leads managers to look for different ways of leading people. Often, they overlook the “Empower others” side because they view it as the “Opposite” side of what they do today. However, if this is a dilemma and not a problem, they can consider both sides of the polarity and find a win-win way.
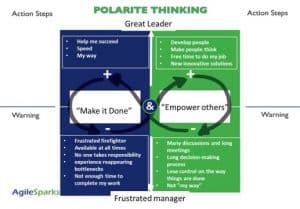
The “Empower others” side makes people “think” and find new innovative solutions, take more responsibility, and feel more commitment & engagement. This gives SM’s and managers free time to do their job, create vision and direction.
To move forward, with using the model managers can sake several “Action Items” that will help them gain the benefits of both sides while keeping in mind “Warning Indicators” that will prevent them from overusing one side. Following the Black arrow from the upper left side which represents understanding the benefits of “make it done” to the lower part with the negative consequences of overdoing it, shows managers to look for benefits of the upper right side of the polarity “Empower others” and avoid the negative consequences of overusing it.
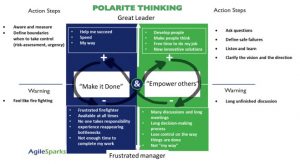
Mapping the polarity alternatives and understanding the downside and the upside of each one of them will help leaders enjoy the benefits of both sides and reduce the consequences that are related to the over-usage of one side.