Actual is a relative term when it comes to business value delivered by a SAFe PI Objective. We had a discussion about this a couple of weeks ago in an Implementing SAFe class and I promised a blog post about this. Here it goes.
Planned Business Value – Making sure Business Owners and the Agile Team are on the same page
Let’s start from the basics though. PI (Program Increment) Objectives are used as a “back briefing” mechanism by Agile Teams on an Agile Release Train to share their plan for the PI and validate that they are indeed focusing on the highest priorities and are planning to deliver objectives that will be valuable for the business.
Business Owners (Business Executive, Product Management, System Architect) circulate between teams during PI Planning and score each PI Objective on a scale of 1..10 based on the business value they ASSUME will be delivered in case this PI Objective is accomplished in the PI.
This becomes the “Planned Business Value (BV)” for that objective.
Actual Business Value – Assessing Business Value based on a Demo of a real solution
Later on, during PI Inspect & Adapt (or earlier during System Demos) the same Business Owners circulate between the teams and score each of these PI Objectives again, this time on “Actual Business Value (BV)”.
What does Actual mean here? Well, in most cases the evaluation is based on seeing a demo of a working solution and still making ASSUMPTIONS about what the actual value would be when the solution meeting this objective will be released and available to real users/customers.
Sorry, but while being much closer, that’s still not ACTUAL business value.
ACTUAL Actual Business Value – Based on released solutions and the outcomes they deliver in the real world
ACTUAL business value delivered can be evaluated only AFTER the solution is released.
On most Agile Release Trains / SAFe contexts the PI I&A is too early to make this evaluation so you could understand why we’re still making assumptions at that stage.
But if we really care about outcomes and delivering value, we shouldn’t close the books on these PI Objectives and the PI at that point. We should get back to it later on and Inspect and Adapt based on real business value delivered.
Adjusting the SAFe Inspect & Adapt to track ACTUAL actual Business Value
If you’re with me, you’re probably asking what can we do about this. What is the right timing to get back and assess the ACTUAL actual Business Value? From a cadence perspective, there are two main ways to do this.
The simplest is to take advantage of the Inspect and Adapt PI System Demo to review the ACTUAL business value delivered by the objectives in the PREVIOUS Program Increment. E.g. if we’re now finishing PI 5, we’re assessing actual business value delivered by the objectives in PI 5 that will be released sometime during PI 6, as well as PI 4 objectives that hopefully got released during PI 5.
More to read:
How do we handle Scope Changes in a SAFe Program Increment?
SAFe includes Scrum – so how come many Scrum practitioners and thought leaders consider it unsafe?
Achieving Business Agility By Implementing Agile at the Organizational level
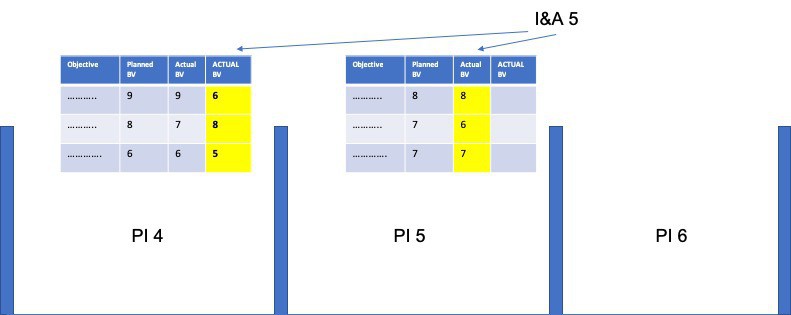
For each one of these PI 4 objectives, now should be a reasonable time to talk about things like – Have customers started to use this solution? Are they happy with it? Did it achieve the impact we had in mind for it? Did we stop incurring the cost of delay we had in mind when prioritizing this? At this point, the 1..10 scores should be data/evidence-driven.
If we AREN’T able to evaluate the actual business value at this point – that means there’s a short-circuit in our empiric feedback loop that we should work on fixing.
If we haven’t released the solution yet, then we should keep the actual score for this objective empty and get back to it in the next PI. This objective should still be a “work in progress” from our perspective.
It’s not DONE until we evaluated the ACTUAL Business Value
You might guess what’s the next aspect of this. Mentioning Work in Progress should be an obvious clue. The Program Kanban has a role in helping us out here as well. Features on the Program-level Kanban shouldn’t be considered DONE until we collected this feedback and evaluated the ACTUAL actual business value on them. They should hang out on the board – may be in an area called “Feedback” or whatever you prefer.
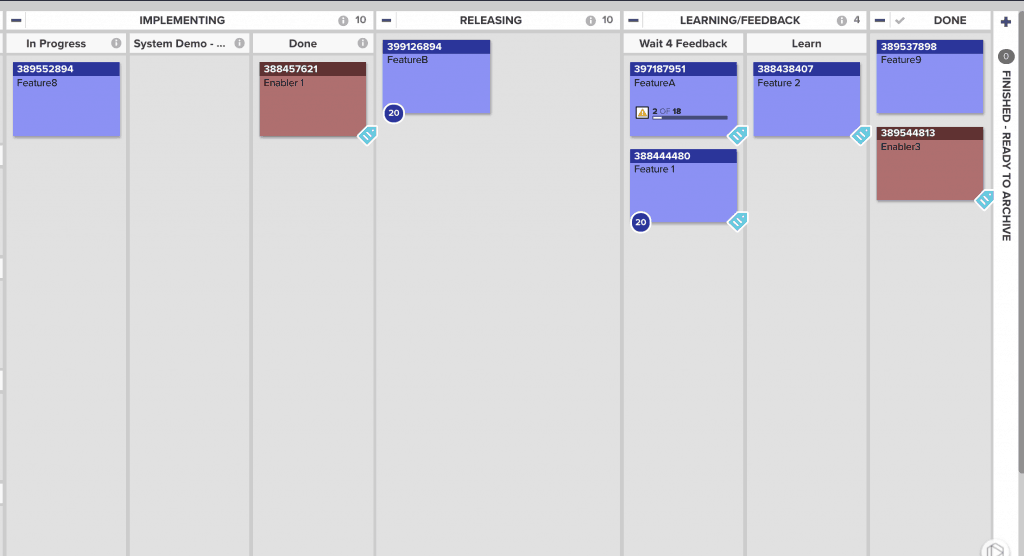
I’ve been recommending this sort of Program-level Kanban Board structure for a long time now. Some of my enterprise-level clients have improved their Product Management practices dramatically through the accountability and follow-through that this practice encourages.
Just think about the impact on Product Management, Business Owners, and Salespeople asking for features, if they know they are accountable for the outcomes from these features after they’re released.
Who’s accountable for delivering the actual business value?
This brings us to an interesting question. Who’s accountable for delivering actual business value? Who’s accountable for delivering ACTUAL actual business value? Is it the Agile Team? Product Management? Business? Sales?
I’ve seen way too many teams frustrated when they deliver the objectives according to what they presented as the plan, and yet the actual business value score is lower than the plan because the Business Owners don’t think as much value will be actually delivered. When we’re moving from assumed actual to actual actual the gap can be even bigger. On one hand, in the spirit of transparency and being focused on value and outcomes rather than output, this is the right way to score the business value. It’s about value delivery rather than tracking to plans. On the other hand, you can probably understand the frustration here.
The way I see it, the only way out of this is to understand that the PI Objective plan vs actual vs ACTUAL isn’t an indication of the individual performance of either one of these roles. It’s an indication of the performance of the whole development value stream including the upstream activities related to choosing and prioritizing features and the downstream activities related to selling the solution, convincing users/customers to use it, implementing it in the field, and operating/supporting it.
That, together with Lean/Agile Leadership that emphasizes principles such as Assuming Variability, Objective evaluation of working delivered systems, and relentless improvement of the whole value delivery cycle, is the key to focusing on learning from these surprises whether they are systemic or repeating or rare exceptions.
A relentlessly improving organization would inspect what’s the trend when it comes to plan vs actual vs actual actual for the whole program and per specific PI Objectives and try to see what it can learn from when the value gap happens and does it happen for a specific type of objectives or in a specific area of the program/business.
It’s all about Value
Value is the goal of Lean and the fast delivery of value is the goal of SAFe. If we’re serious about that, We should raise our game when it comes to managing value as a first-class citizens in SAFe. Business value on PI objectives is the perfect place for doing exactly that.
So, Next time you have PI Inspect & Adapt, don’t just look at the PI you’re finishing just now, take a look at the objectives from the previous PI as well. And on your Program-level Kanban only consider features done after evaluating actual business value delivered, ideally based on quantifiable metrics.
I love it when discussions in class drive me to write up some of my experiences, tips, and tricks for the blog. Awesome kudos to my students, now SPCs off to implement a healthy and value-oriented SAFe in their organizations!